What is USB?
USB means Universal Serial Bus and it is used for connecting peripherals to computers or smart phones, allowing for data transfer video display and power delivery.
- USB-A: The classic rectangular connector found on computers and TVs. Used for data and power transfer.
- USB-B: Square-shaped, mainly for printers and cameras. Prevents host-to-host connections.
- Mini-USB: Smaller than USB-B, once common in early mobile devices and cameras. Now mostly legacy.
- Micro-USB: Slimmer than Mini-USB, widely used in mobile devices. Supports USB OTG for connecting peripherals.
- USB-C: The newest and most versatile. Reversible, fast (up to 80 Gbps), and powerful (up to 240W). Supports data, charging, and video.
USB Male Connectors:
- Found on the ends of USB cables and dongles.
- Plugs into USB ports on devices.
USB Female Ports:
- Located on devices like computers, peripherals, and USB extension cables.
- Designed to accept male USB connectors.
- In essence, male connectors fit into female usb ports, enabling connections and data transfer between devices
Identifying USB Type
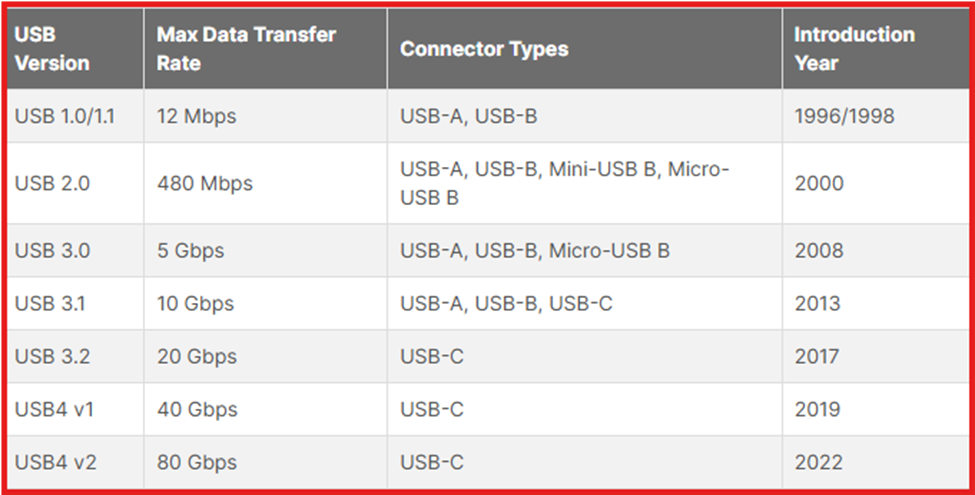
Since USB was introduced, it has been great involved in our daily life. Major different are speed, power delivery and compatibility across the devices. For the details, please see below photo, you will be clear on USB version.
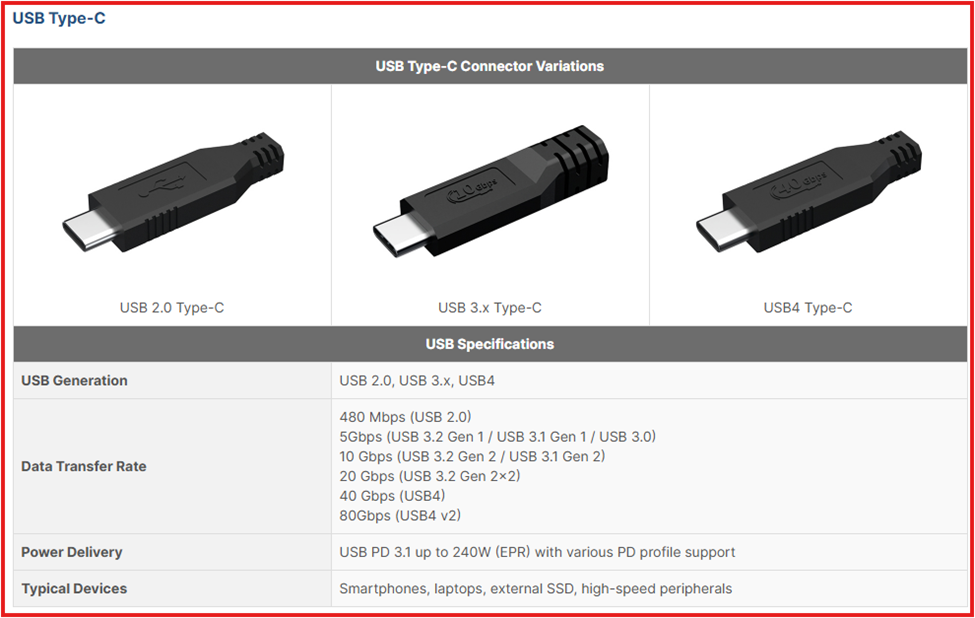
USB-C
USB Type-C is a reversible connector used for both hosts and peripherals. It supports USB 2.0 to 4.0, offering speeds up to 80 Gbps and power delivery up to 240W—ideal for fast charging, data transfer, and video output.
USB-A
USB Type A is a flat, rectangular connector commonly found on computers, TVs, and gaming consoles. It supports one-way data and power transfer from host to device and works with USB 2.0, 3.0, and 3.2 standards.


USB-B
USB Type B has a square-like shape used mainly for printers and cameras. Its design prevents connecting two host devices, protecting hardware. Though newer connectors are emerging, USB-B remains vital for safe, reliable peripheral connections.


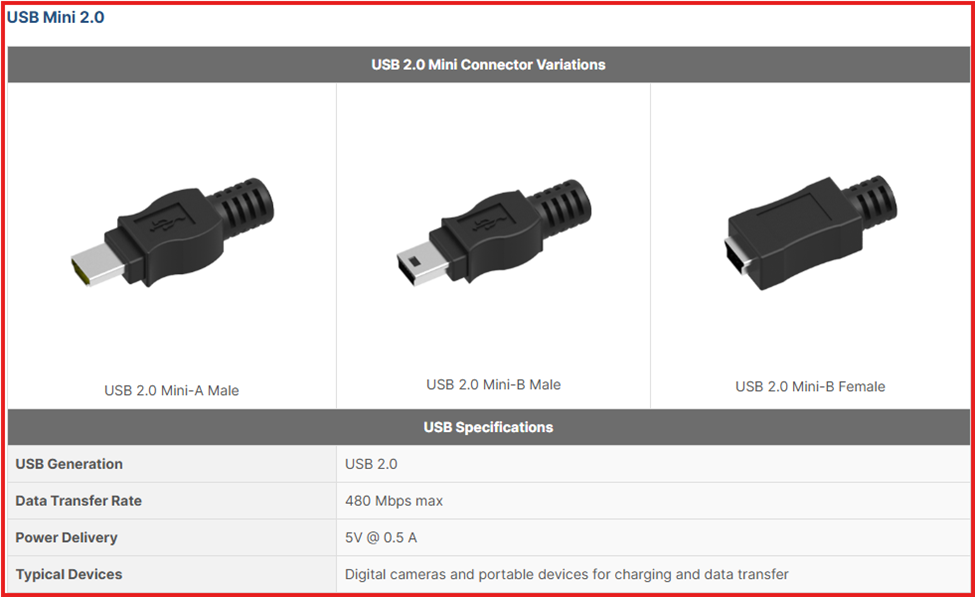
USB Mini
Mini USB connectors are compact 5-pin plugs once common in early mobile phones and cameras. Mini B supported USB OTG, letting devices act as hosts. Mini A was rarer, used in some portable gadgets. Both are now legacy connectors, replaced by micro USB and USB-C.
USB Micro
Micro USB B is a compact connector used in slim mobile devices for charging and data transfer. It supports USB OTG, letting devices connect to peripherals like drives and cameras. Though now largely replaced by USB-C, it remains common in many portable electronics.


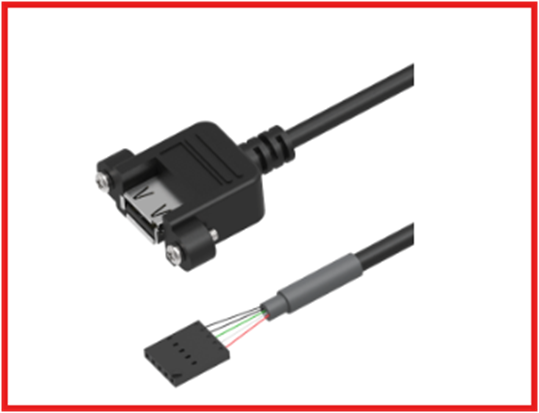
USB Motherboard Connector USB 2.0 cables often use crimp header connectors to connect with motherboard. 5 pin and 10 pin header are the most common seen configurations

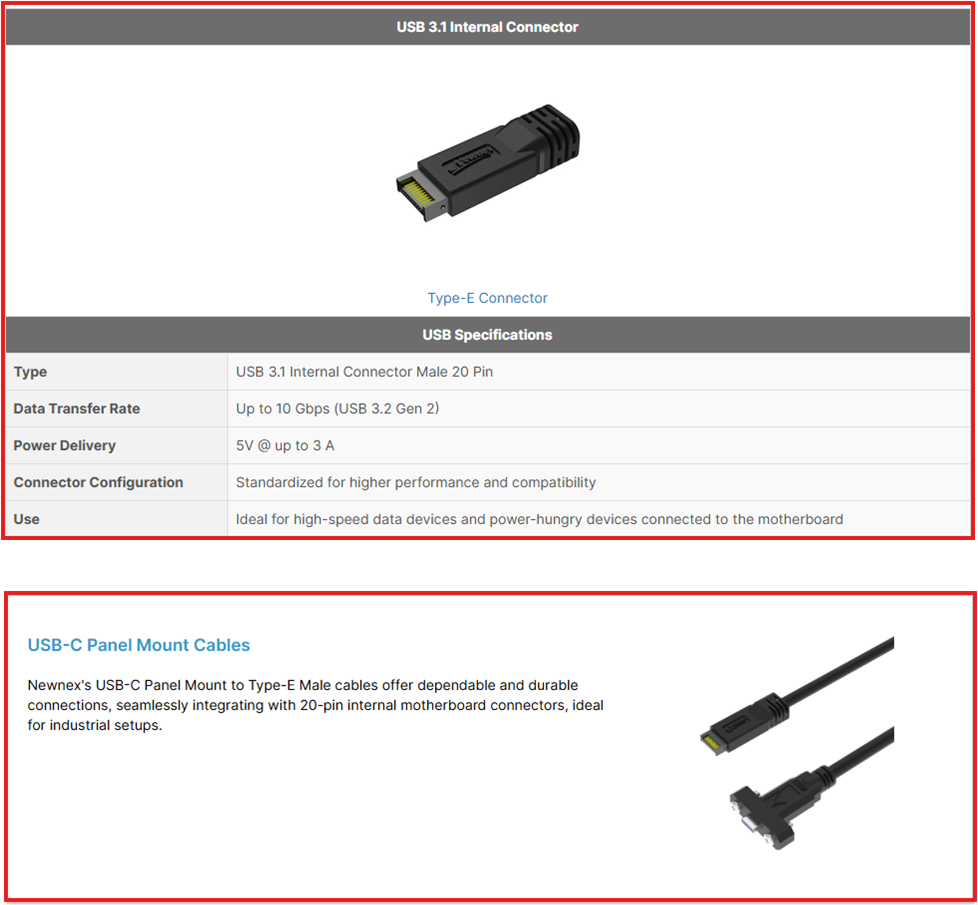
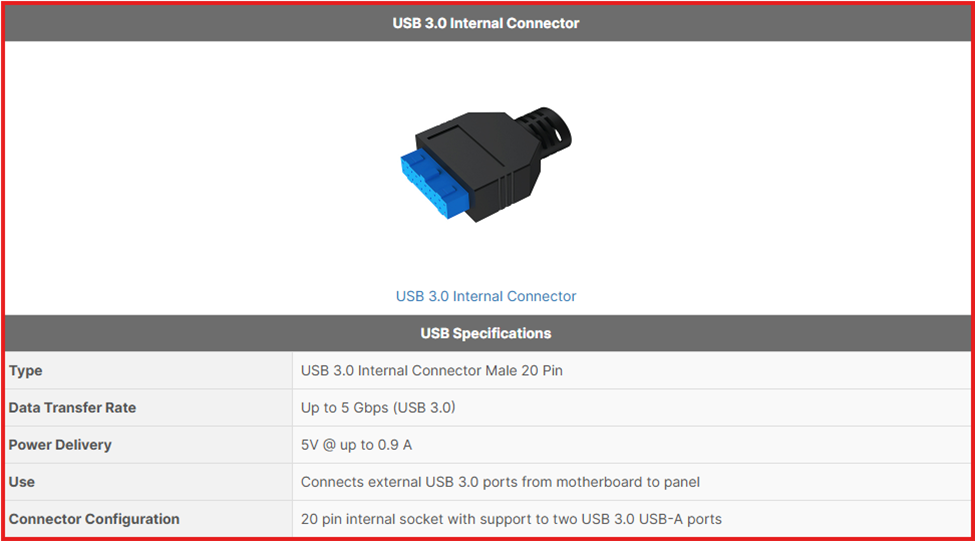
USB 3.0 Internal Connector
This 20-pin connector links front panel USB ports to the motherboard, supporting two USB 3.0 ports at 5Gbps without sharing bandwidth. It ensures high-speed data transfer and signal integrity for SuperSpeed USB connections.

Type-E Key-A Header
In contrast, the USB 3.1 internal connectors build upon the USB 3.0 design by offering a more compact form factor and a stronger mechanical latch. While retaining the 20-pin header for single Type-C or dual Type-A connections, it introduces a 40-pin version to support two full-feature Type-C ports. These connectors ensure that the latest USB standards are accessible from the front of PC cases, facilitating easy and efficient connection for a variety of devices.